Murch Randall S., So William K., Buchholz Wallace G., Raman Sanjay, Peccoud Jean.
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2018
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2018.00039/full
In our view, their focus on the security risks of Big Data in the life sciences falling into just two major categories, i.e., inappropriate access to data and analytic technologies through vulnerabilities in the data and cyber infrastructure; and, the use of Big Data technologies to integrate current data and enable the design of a harmful biological agent should be revisited and refined. Thanks to this team’s efforts, not only do we have a useful topology of Big Data, the beginnings of a structure for thinking about security implications at the bio-cyber interface (Technical, Legal, Institutional and Individual) and a set of high-level recommendations for a path forward.
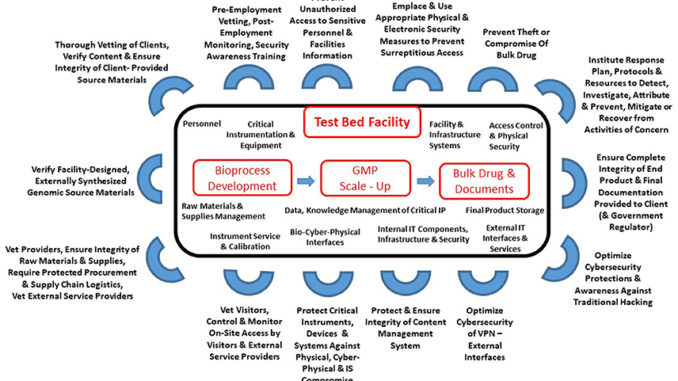
Concomitantly, experts are increasingly recognizing that biomanufacturing itself is potentially vulnerable to unwanted or illicit activities which could result in damaging outcomes. These could include the theft of intellectual property, disruption of the supply chain, manipulation of the bioprocess development and bioproduction, cyberattacks on key information technology components and cyberphysical interfaces, the corruption of critical data and manipulation of security systems and infrastructure upon which secure and safe facility operations are dependent.